Green Glamour: The Rise of Eco Friendly Lab Grown Diamond
For centuries, diamonds have symbolised love, luxury, and timeless beauty. Traditionally mined from deep within the earth, these sparkling stones have long held a place in engagements, milestones, and heirlooms. But as environmental awareness grows and ethical concerns around diamond mining come to light, consumers are beginning to question what lies beneath the surface of their jewellery.
Enter lab grown diamonds a revolutionary alternative that's challenging the status quo of the diamond industry. Created using advanced technology that replicates the natural conditions under which diamonds form, lab grown diamonds are chemically, physically, and visually identical to mined ones. The key difference? Their origin, and increasingly, their impact.
Today’s consumers are not just drawn to brilliance and clarity, they want their purchases to reflect their values. As sustainability becomes a global priority, eco-conscious buyers are turning to lab grown diamonds as a cleaner, more ethical option. This shift is transforming not only what we consider beautiful, but also what we consider responsible.
In this blog, we’ll explore the rise of lab grown diamonds as a sustainable choice, examine how they compare to traditional diamonds environmentally and ethically, and look ahead to their role in the future of conscious luxury.
What Are Lab Grown Diamonds?
Lab grown diamonds, also known as synthetic or cultured diamonds, are real diamonds creat in a laboratory rather than extracted from the earth. Though they are man made, they are chemically, physically, and optically identical to natural diamonds. To the naked eye and even under a jeweller’s loupe lab grown diamonds are indistinguishable from their mined counterparts.
In recent years, lab grown diamonds have gained significant traction, not only for their sustainability but also for their affordability. Since they avoid the complex and costly logistics of mining, lab grown diamonds are often price 20–40% lower than their mined counterparts, making luxury more accessible.
Define lab grown diamonds and how they’re created (HPHT and CVD methods).
- High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT)
Lab grown diamonds are man-made diamonds that are produce in control laboratory environments using cutting-edge technology that replicates the natural processes under which diamonds form in the earth. These diamonds are chemically, physically, and optically identical to mined diamonds; the only difference is their origin.
The HPHT method replicates the natural geological conditions under which diamonds form in the Earth’s mantle namely, extremely high pressure and temperature. It was the first successful method develope to produce synthetic diamonds and is still widely used today.
How It Works:
- A tiny diamond seed (a small piece of carbon crystal) is place inside a carbon source, typically graphite.
- This setup is enclosed in a specially design press that can generate immense pressure (around 5–6 GPa, or 725,000 psi) and high temperatures (over 1,400°C).
- Under these conditions, the carbon melts and starts to crystallise around the seed.
- Over the course of several days to weeks, a rough diamond slowly forms around the seed.
- The diamond is then carefully cool to prevent stress fractures.
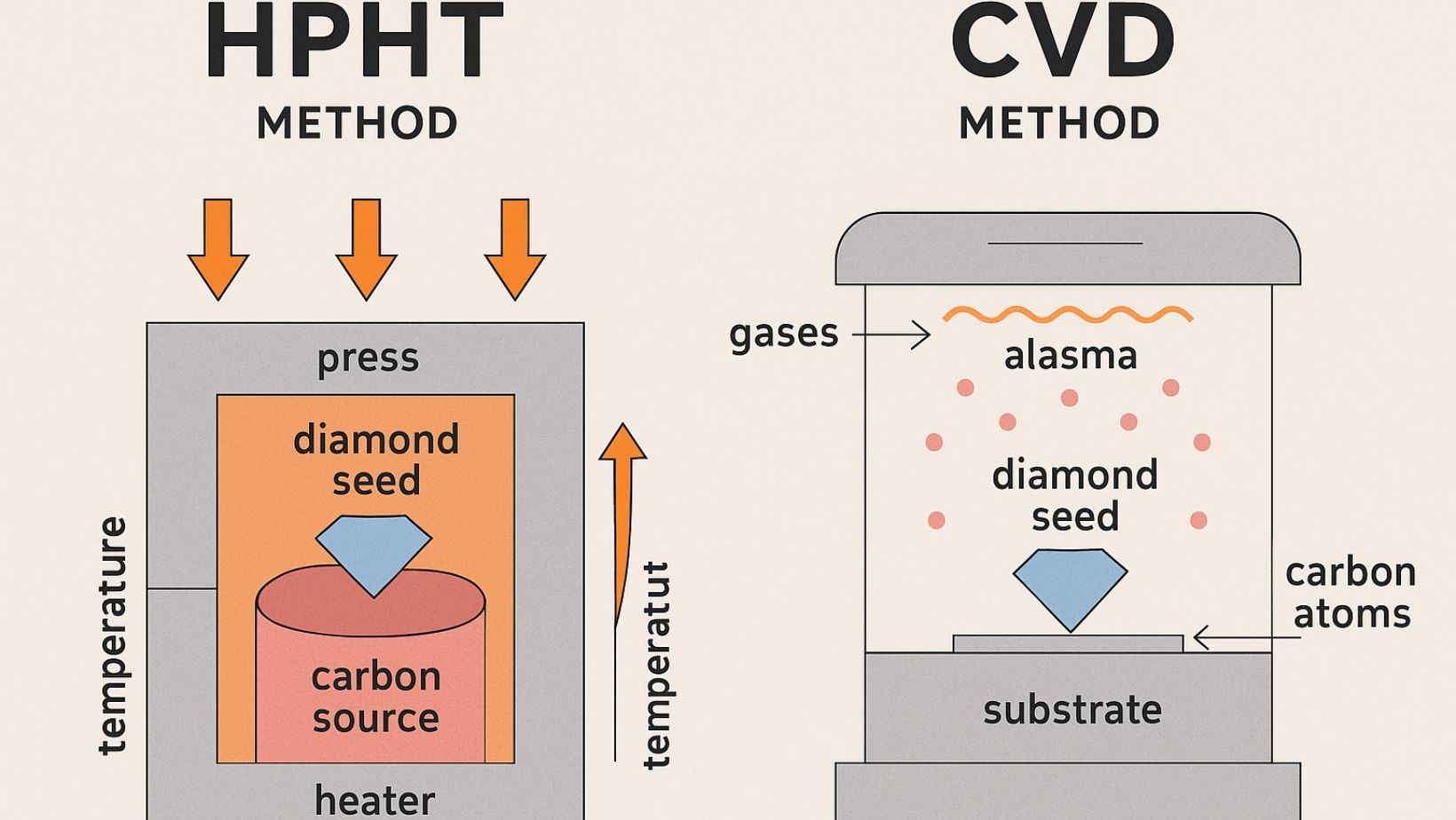
2. Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD)
CVD is a more modern and efficient method that allows greater control over the purity and structure of the diamond. It's especially popular for producing high-quality diamonds for both jewellery and industrial uses.
How It Works:
- A thin diamond seed is place inside a sealed vacuum chamber.
- The chamber is fill with a carbon-rich gas, typically methane, along with hydrogen.
- The gases are heat using microwaves or lasers to temperatures around 800–1200°C.
- This causes the gas molecules to break apart, releasing carbon atoms.
- These atoms settle onto the seed layer by layer, forming a diamond crystal over several weeks.
The Environmental Impact of Diamond Mining

While natural diamonds may symbolise love and commitment, their extraction often leaves a very different legacy on the environment. Traditional diamond mining is an intensive, industrial process that can result in significant and long lasting ecological damage. To understand why lab-grown diamonds are gaining favour as the greener choice, it’s important to first look at the environmental costs of conventional diamond mining.
Diamond mining often involves large-scale excavation of the earth, especially in open-pit and alluvial mining operations. These processes require removing massive amounts of soil and rock. Deforestation: Vast areas of forest are cleared, disrupting ecosystems. Loss of biodiversity, Wildlife habitats are destroyed, displacing or endangering native species. Soil erosion. Exposed soil becomes vulnerable to erosion, degrading the landscape permanently. Mining operations consume large volumes of water, which is especially damaging in regions where water is scarce.
Sediment runoff and chemical waste from mining can contaminate rivers and groundwater. Toxic substances such as mercury and cyanide (used in other types of mineral extraction but sometimes present in diamond mining zones) can poison aquatic life and harm nearby communities. In alluvial mining, riverbeds are disrupted to extract diamonds, altering the natural flow of rivers and reducing water quality downstream.
Why Lab Grown Diamonds Are Greener
Lab grown diamonds are gaining popularity not only for their beauty and affordability but also for their strong environmental credentials. As concerns about climate change, ecological destruction, and overconsumption grow, more consumers are turning to sustainable alternatives. Lab grown diamonds offer a way to enjoy the brilliance and symbolism of a diamond while significantly reducing environmental harm. But what makes them a truly greener option?

Firstly, lab grown diamonds eliminate the need for mining, one of the most environmentally damaging aspects of the traditional diamond industry. Mining requires the removal of massive amounts of eart. Leading to deforestation, habitat destruction, soil erosion, and the permanent alteration of landscapes. In contrast, lab grown diamonds are creat in controlled indoor facility using advance technology, leaving natural ecosystems untouch.
Another major environmental benefit is the lower carbon footprint of lab grown diamonds. The mining process relies heavily on diesel-powered machinery and long global supply chains, resulting in high greenhouse gas emissions. Lab grown diamonds, particularly those produced with renewable energy sources, have a significantly smaller carbon footprint.
Ethical Benefits of Lab Grown Diamonds
Beyond their environmental advantages, lab grown diamonds also present a powerful ethical alternative to traditionally mined diamonds. The conventional diamond industry has long faced scrutiny over issues such as forced labour, conflict funding, and human rights abuses. Lab grown diamonds offer a transparent, responsible path forward, ensuring that beauty is not tarnish by exploitation.
One of the most significant ethical concerns in the natural diamond industry is the issue of "blood diamonds" or conflict diamonds. These are diamonds mine in war zones and sold to finance armed conflict against governments, often contribute to violence. Human suffering, and political instability. Although global efforts like the Kimberley Process were introduce to reduce the trade in conflict diamonds, many critics argue that the system lacks enforcement and has serious loopholes.
Lab grown diamonds, by contrast, are produce in highly controlled laboratory settings. Often in country with strong labour and safety regulations such as the United States, Canada, or parts of Europe. This ensures that full traceability and transparency are maintain in the supply chain. It can be ensure that the diamond is made without the use of child labour, unsafe working conditions, or unfair wages. There is no ambiguity, no hidden exploitation—just a clear, ethical process from start to finish
The Future of Lab Grown Diamonds

As consumer awareness grows and technology continues to advance. Lab-grown diamonds are poise to play a significant role in the future of the jewellery industry and beyond. What was once considered a niche or novelty product is rapidly becoming mainstream, with increasing demand driven by sustainability, ethical concerns.
One of the biggest indicators of the future potential of lab grown diamonds is their surging popularity among younger consumers, particularly Millennials and Gen Z. These generations are far more likely to prioritise environmental and ethical considerations when making purchases. Lab grown diamonds align perfectly with these values, offering a guilt-free alternative that still delivers the same brilliance and durability as mined diamonds.
From an industry perspective, jewellery brands and retailers are increasingly embracing lab grown stones. Major names like Pandora and De Beers (through its Lightbox subsidiary) have introduced lab grown diamond collections, recognising the shift in market demand. High-end designers and engagement ring specialists are also offering lab-created options, normalising them within luxury and bridal markets.
Conclusion
Lab grown diamonds are not just a passing trend; they represent a profound shift in the way we think about luxury, sustainability, and ethics. With their remarkable ability to combine beauty, durability, and environmental responsibility, lab grown diamonds offer a compelling alternative to traditional mined diamonds. As we continue to face the growing challenges of climate change and resource depletion, these eco-friendly diamonds are helping to pave the way for a more sustainable and ethical future.
The benefits of lab grown diamonds are clear: lower environmental impact, reduced carbon emissions, minimal water usage, and no human exploitation. Their growing popularity is a testament to how consumers are increasingly prioritising the planet and people over the status quo. As technology advances, lab grown diamonds will only become more accessible, diverse, and impactful, shifting the entire jewellery industry towards a cleaner, greener future.
Designed to Dazzle Your Custom Design Ring
At DiamondsByUK, we believe every love story deserves a stone as unique as the person wearing it. Our custom design service invites you to bring your vision to life from selecting the perfect Diamond to choosing the setting, shape, and style that reflect your individuality. Whether you're inspired by timeless elegance or modern minimalism, our expert craftsmen work closely with you to create a one-of-a-kind piece that captures your sentiment and sparkles with personal meaning
Shop Now
FAQS
1. Is it worth buying a lab grown diamond?
Because of this, lab created diamonds cost less to buy than natural diamonds. However, a lab diamond is still 100% authentic and identical to a scintillating, beautiful mined diamond, which means it is worth something: it is a valuable, desirable and still very rare product.
2. Is a lab grown diamond a cubic zirconia?
No, a lab grown diamond is not the same as cubic zirconia (CZ). While both are created in labs, they are distinct materials with different chemical compositions and properties. Lab grown diamonds are real diamonds, chemically identical to naturally mine diamonds, while CZ is a diamond simulant made from zirconium dioxide.
3. What type of lab diamond is best?
The best grade of lab grown diamonds is determine by the 4Cs: color, clarity, cut, and carat weight. The highest color grade for lab grown diamonds is D (colorless), followed by E and F. The best clarity grade is IF (internally flawless), followed by VVS1 and VVS2 (very, very slightly included).
4. Are lab grown diamonds more environmentally friendly?
Yes, lab grown diamonds are generally consider more environmentally friendly than mine diamonds due to significantly reduced environmental impact during production and extraction. Lab grown diamonds require less land disturbance, water, and energy, and produce less waste and carbon emissions compared to mining operations.
5. Are lab diamonds actually ethical?
Lab grown diamonds generally hold less resale value than natural diamonds due to a combination of factors, including their availability, perceived rarity, and the established market for natural diamonds. While lab grown diamonds offer a cost effective alternative, their potential for resale is often lower, particularly compared to natural diamonds.



